Up to now, science knows about 280 types of worms that can develop and live in the human body, parasitizing in many different organs and tissues. The frequency of human worm infection depends on the climatic and socio-economic conditions of each specific territory (in underdeveloped countries, especially in the tropics and subtropics, the degree of infection. parasites are much higher than countries with developed economies).
Ways of human infection with helminths
- Biohelminthiasis (infection from animals).
- Infectious helminthiasis (spread from person to person).
- Geohelminthiasis (a disease caused by parasites that carry out one of their life cycles on earth).
Factors influencing manifestations of helminthiasis
- How parasites enter the body;
- The degree of adaptation of helminths to the human body;
- Density (number) of parasitic individuals in the population;
- Worm habitat (parasitic in tissue that lives in the thickness of soft tissues, and brightly colored ones live in the lumens of hollow organs). Some helminths at different stages have both a luminous and tissue form. The larval and developmental stages of the worms, as a rule, cause more pronounced pathological changes.
In the absence of reinfection, the number of adult parasites in the human body does not increase. This feature significantly distinguishes helminthic invasions from diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa.
Worms in humans: symptoms
Worm disease is just a disease characterized by 2 stages of the disease (acute, from two weeks to two months) and chronic (from a few months to several years).
Symptoms of the acute phase of helminthiasis
The first signs of the disease can appear at different times (most commonly after 2-3 weeks, with roundworm - after 2-3 days, and with filariasis, timeincubation can last 6-18 months).
During the acute phase of parasitic infestation, the most characteristic symptom is an allergic reaction (antibodies are produced with antigens of a migrating parasitic larvae). Usually in people infected with worms, an itchy skin rash, prone to recurrence, regional lymph nodes increase, systemic or local edema, muscle and joint pain. In addition, the migratory parasitic larvae can cause chest pain, cough, choking, dyspepsia, nausea and vomiting.
At the same time, the acute phase of helminthiasis can be accompanied by more serious disorders (severe forms of pneumonia, hepatitis, atopic myocarditis, hepatosplenomegaly (liver and spleen). enlargement), meningitis).
The number of eosinophils in the blood is increased (eosinophilia) and the quantitative ratio is normal between disturbed protein fractions (dysproteinemia).
Signs of chronic helminthiasis
Symptoms of the chronic stage depend directly on which organs are "inhabited" by the parasite, as well as their size and number playing an important role. Therefore, when parasitized in the intestines of single individuals, the disease may be asymptomatic (except for very large parasitic infections). Characteristic signs of the chronic course of intestinal helminthiasis are digestive disorders. In children, pain syndrome and neurasthenia are more pronounced. With a massive infiltration of roundworm, the development of intestinal obstruction, obstructive jaundice and pancreatitis are possible.
Therefore, when parasitized in the intestines of single individuals, the disease may be asymptomatic (except for very large parasitic infections). Characteristic signs of the chronic course of intestinal helminthiasis are digestive disorders. In children, pain syndrome and neurasthenia are more pronounced. With a massive infiltration of roundworm, the development of intestinal obstruction, obstructive jaundice and pancreatitis are possible.
Consume all substances necessary for their living from the host body, helminths cause digestive disorders, impair the absorption of vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins and fats. At the same time, the worms' residue inhibits the normal intestinal microflora and reduces the body's immune force.
In people with helminthiasis, due to a weakened immune system and enhanced cell division (a consequence of the constant restoration of tissue damaged by the parasite), the risk ofMalignant tumors increased significantly.
Types of helminths that are parasitic in the human body
The causative agent of human helminths are 2 types of worms: nematodes (nematodes) and flatworms (tapeworms and tapeworms).
Roundworm
Pinworms
Intestinal helminthiasis are small cavity worms (up to 10mm) that are gray-white in color. Infection occurs by mouth (through the mouth). The reason for this is dirty hands. The eggs of the parasite can stay underground, on the wool of infected animals, unwashed vegetables and fruits, etc. v. At the same time, with intestinal helminthiasis, cases self-infecting frequently (especially in children), caused by scratching of the itchiness and subsequent swallowing of eggs.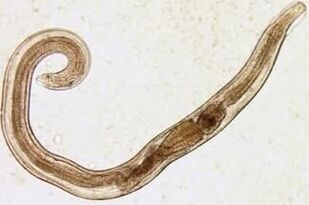 Pinworm larvae develop within two weeks in the digestive tract. As an adult, the worms parasitize in the lower part of the small part and the upper part of the colon.
Pinworm larvae develop within two weeks in the digestive tract. As an adult, the worms parasitize in the lower part of the small part and the upper part of the colon.
Even in the larval stage, pinworms begin to harm the host's body, creating enzymes that irritate the intestinal wall and lead to the development of the inflammatory process. The adult parasite attaches to or penetrates the deeper layers of the intestinal mucosa, disrupts its integrity and contributes to attachment to secondary bacterial infection. In the case of pinworms puncture the wall of the small intestine, peritonitis can develop. In addition, due to the stimulation of the intestinal receptors, the motor and secretory functions of the gastrointestinal tract are disrupted, leading to the formation of inflammatory diseases of the stomach, intestines, etc. v. In childhood, long-term intestinal helminthiasis can cause neurological disorders and slow physical development.
Roundworm
Roundworm is a large, reddish-yellow axial parasite, up to 40 cm long (female) and 15-25 cm (male) in adulthood. Without the need for suction cups or other tying devices, the roundworm can move independently towards the food mass. The eggs produced by the female parasite are excreted with the feces.
Roundworm infection occurs when mature eggs are swallowed up with water or unwashed vegetables that have contaminated soil. Once the eggs enter the intestine, adult larvae emerge from them. Then, penetrating the intestinal wall, they reach the heart through the bloodstream, and from there they enter the lungs. Through the lung alveoli, the respiratory roundworm larvae enter the oral cavity again. After swallowing several times, the parasite reaches the small intestine, where it develops into an adult. The worm lives for 12 months, then dies and is excreted with the feces. In the gut of a host, both one and a few hundred individuals can live.
During their period of existence, roundworms, endowed with a helical mobility, are able to penetrate even the narrowest openings. This feature of the parasite often leads to the development of quite serious complications (obstructive jaundice or pancreatitis). Allergens secreted by ringworm can cause severe allergic reactions. Large numbers of adults can cause intestinal obstruction, worms entering the respiratory tract sometimes causing suffocation.
Vlasoglav
Vlasoglav, the causative agent of trichocephalosis, is a white helminth that parasites in the initial segment of the large intestine and has a size of 4-5 cm. This parasite eats blood and tissues of the rectal mucosa.
Whip eggs are laid by females on the intestinal wall with feces. Their development takes place in the environment (preferably in the soil). Eggs have the larvae of the ripe parasite which enter the body through means of spices, through dirty hands, unwashed water or vegetables.
With small numbers of worms, trichocephalosis has no symptoms. In the severe stage (with mass invasion) the patient develops severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, sometimes accompanied by rectal prolapse. This condition is often observed in debilitated children. With an average course of trichocephalosis, a child can develop a delay in growth.
Trichinella
The causative agent of helminthiasis is a small round helminth with a length of 2-5 mm. Infection occurs when eating poorly roasted meat (pork, bear meat, wild boar). Penetrates the intestine, larvae of the adult parasite in 3-4 days to the state of a sexually mature individual. The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By penetrating the intestinal wall, the larvae enter the bloodstream and are carried to all organs of the human body, settling in the muscles. In this case, the respiratory and facial muscles as well as the folding muscles of the extremities are most often affected.
Penetrates the intestine, larvae of the adult parasite in 3-4 days to the state of a sexually mature individual. The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By penetrating the intestinal wall, the larvae enter the bloodstream and are carried to all organs of the human body, settling in the muscles. In this case, the respiratory and facial muscles as well as the folding muscles of the extremities are most often affected.
During the first days after invasion, patient complained of abdominal pain. Then, about 2 weeks, the body temperature rises to 39-40 degrees Celsius, an itchy skin rash, muscle pain and swelling of the face. During this period, in the case of a massive infection, there is a significant risk of death. After about a month, the patient recovered. The parasite is enveloped in a spiral form, after which it dies within two years.
Hookworms and nekator
These two parasites are similar in biological characteristics, as well as the diseases they cause. In this regard, it is common to combine them under a common name (hookworm). Worms, up to 10-15 mm long, are parasitic at 12-p. intestine. It should be noted that this is one of the most common cases, but at the same time, parasites are quite rare. Worm larvae enter the human body through the skin when in contact with contaminated soil. Furthermore, when they enter the bloodstream, they, like roundworms, travel to the lungs, then through the bronchi, along with phlegm, into the digestive tract. Ankylostoma parasitizes in the intestine, attaching itself to the intestinal wall. This parasite feeds only on blood, bites through blood vessels that penetrate the mucous membrane, injects an anticoagulant component into it. On average, an adult can absorb 0. 5-0, 35 ml of blood per day. Therefore, the most characteristic symptom of this helminthiasis is iron deficiency anemia, as well as a change in protein fractions (dysproteinemia).
Worms
Wide ribbon
This is one of the largest helminths, up to 10 - 20 meters in length. Disease caused by this parasite is called diphyllobothriasis. The worm's development cycle begins with freshwater fish or crustaceans. The larvae, which invade the human body, are the ultimate owners of the broad tapeworm, along with infected eggs or fish fillets. Reaching the small intestine, the parasite attaches to its wall and develops into an adult within 20-25 days.
Diphyllobothriasis disease occurs on the basis of gastrointestinal disturbances and B12 deficiency anemia.
Liver fluke
The small liver fluke parasite is a flat worm with a length of 7-20 mm. It should be noted that more than 50% of cases of liver fluke (also known as cat fluke) occur in Russian residents. Larvae of the parasite begin to develop after the eggs enter fresh water (from snails that have swallowed them). Then they enter the fish body (carp, crayfish, sesame, perch). Human infection occurs from eating contaminated fish meat that has not been exposed to sufficient heat treatment. The larvae of the hepatomegaly from the small intestine penetrate the biliary tract and into the gallbladder, fixed there with the aid of two suction cups.
During the acute phase of helminthiasis, the patient experiences pain in the upper abdomen, elevated body temperature, nausea, muscle pain, diarrhea, and a skin rash. The chronic course of eye stone disease is manifested by symptoms of hepatitis, cholangitis, cholecystitis, gastrointestinal disturbances, neurological disorders, weakness and fatigue. The parasite leads to the development of irreversible changes, and even after expulsion, the patient does not undergo chronic inflammatory processes and dysfunction.
Cow and Pig tapeworm
These parasites, which have an almost identical structure, reach a length of 5-6 meters. Teniarinhoses and teniasis infections are caused by eating infected Finnish meat or pork (one of the intermediate forms of helminthiasis). The viable Finns, presented as a white bubble of the size 0. 5 cm, attach to the wall of the human small intestine and transform into an adult for 3 months. Ice parasites, consisting of more than 2000 segments, are constantly growing. In this case, the final segments, which contain eggs, break apart and move independently along the large intestine to the anus, then crawl out of the anus, or be discharged to the outside environment with feces. The most characteristic symptoms of helminthiasis are a gastrointestinal disorder.
Echinococcus
For this type of parasite, the human is an intermediate host. Worms parasitize on the human body in the form of the Finns. The final owner of echinococcus is a wolf, a dog, or a cat. 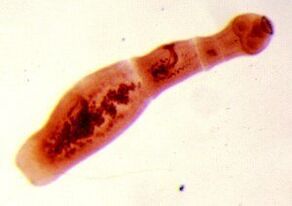 Infection occurs through contact with animals and objects in environments containing Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, sex cells (six-hook larvae) develop from them. From the intestines, they enter the bloodstream and are carried throughout the body.
Infection occurs through contact with animals and objects in environments containing Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, sex cells (six-hook larvae) develop from them. From the intestines, they enter the bloodstream and are carried throughout the body.
The "preferred" parasitic sites for worms are the liver and lungs. By settling in these organs, the larvae transform into a Finn (echinococcal follicle), whose size gradually increases, begins to destroy neighboring tissues. Often, echinococcosis during diagnosis is mistaken for a tumor of benign or malignant origin. In addition to mechanical action (compression of organs and blood vessels), sometimes hydatid cyst rupture occurs. This can cause toxic shock or the formation of many new cysts.
Globe
This parasite, considered a type of echinococcus bacteria, is responsible for one of the most dangerous helminthiasis (alveolar disease), of a similar severity to cirrhosis and cancer. liver letter. Infection occurs when oncospheres (eggs with adult larvae) enter the intestines. There, the embryo leaves the egg and enters the intestinal wall, entering the bloodstream. Furthermore, according to the bloodstream, the parasite spreads to all tissues and organs of the body (usually located in the liver). There, the main stage of development begins in the larvae (poly-chamber bubbles, blood cells are formed). Each cavity holds the embryonic tip of the parasite, continuing to develop gradually. Laurocysts are very active formations, constantly growing due to expanding bubbles, and also potentially growing into the liver, like cancer metastases. Necrotic changes caused by disorders of blood vessel activity undergo necrotic changes in neighboring tissues. Spreading to neighboring structures, the pneumococci form filamentous nodes with polycystic bubbles. This condition can last for several years, and therefore it requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
Diagnosis of helminth infestation involves the following activities:
- looks at the medical history carefully, helping to find possible causes of infection;
- laboratory tests for feces, blood, intestinal contents 12p, rectal and perianal mucus, muscle tissue, lung sputum, bile. Analysis can reveal parasite eggs, fragments or fragments. At the same time, an increased content of eosinophils in the blood is also an indication of the presence of helminthiasis.
- when diagnosing larval stage or tissue parasitic disease, serological studies were performed (ELISA, RSK, indirect agglutination reaction, immunofluorescence analysis, etc. ).
- ultrasound, CT examination and endoscopy are prescribed to detect helminths affecting liver tissue.
Human worms: treatment
During the acute phase of parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed detoxification and desensitization therapy. In severe cases of disease (liver fluke, helminthiasis), glucocorticoids are used according to medical indications.
As a drug of specific therapy, taking into account the nature of the pathogen, special anthelmintic chemotherapy agents are prescribed.
In parallel, the patient is advised to take antihistamines and intestinal solvents. The final stage of treatment involves the use of probiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora.
A special diet is also prescribed (food should be easy to digest and low in fat).
During treatment with anthelmintic drugs, the patient must strictly adhere to personal hygiene (to avoid reinfection). Also, for many helminthiasis, all family members and those in regular contact with the infected person must be treated.
Prevention of helminthiasis
- Keep personal and public good hygiene;
- Strictly comply with the cooking technology;
- Regular inspection and preventive treatment of pets;
- Thoroughly wash fresh vegetables, fruits and herbs;
- Proper handling of river fish;
- Avoid raw, slightly salted, and dried fish.






































